Measles: signs and symptoms
Learn more about what the measles virus is and how measles spreads
February 20, 2025
What is measles?
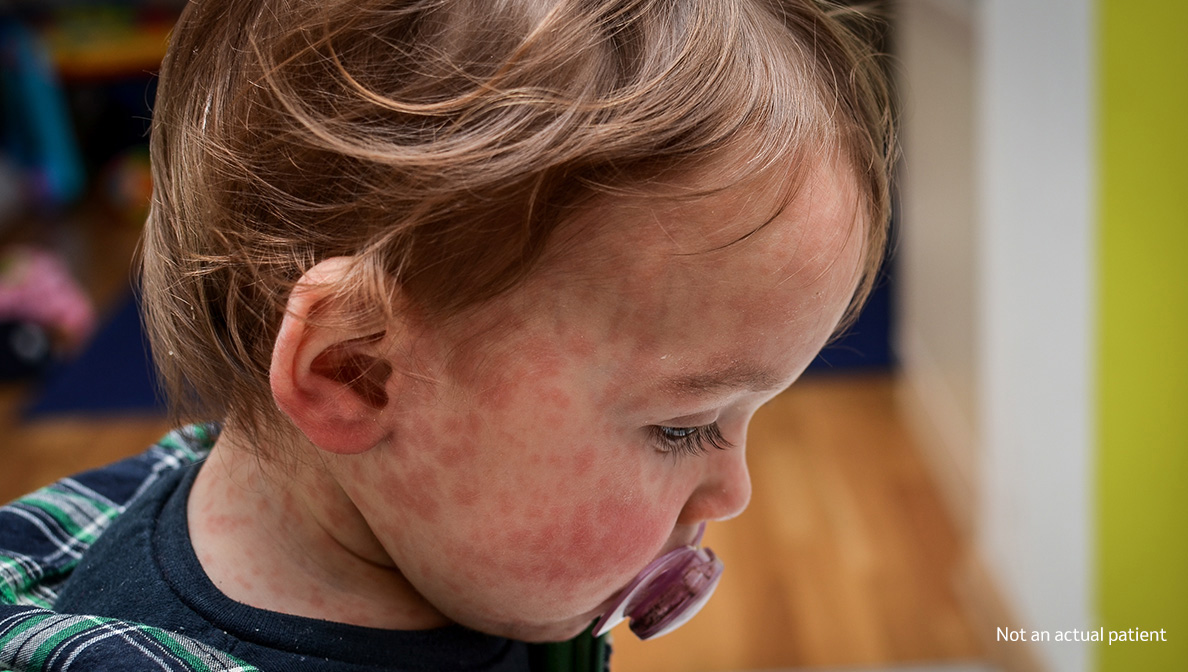
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease that can affect people of all ages but is most common in children. Measles spreads through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Symptoms appear 10 to 14 days after contact with the virus.
Common measles symptoms include:
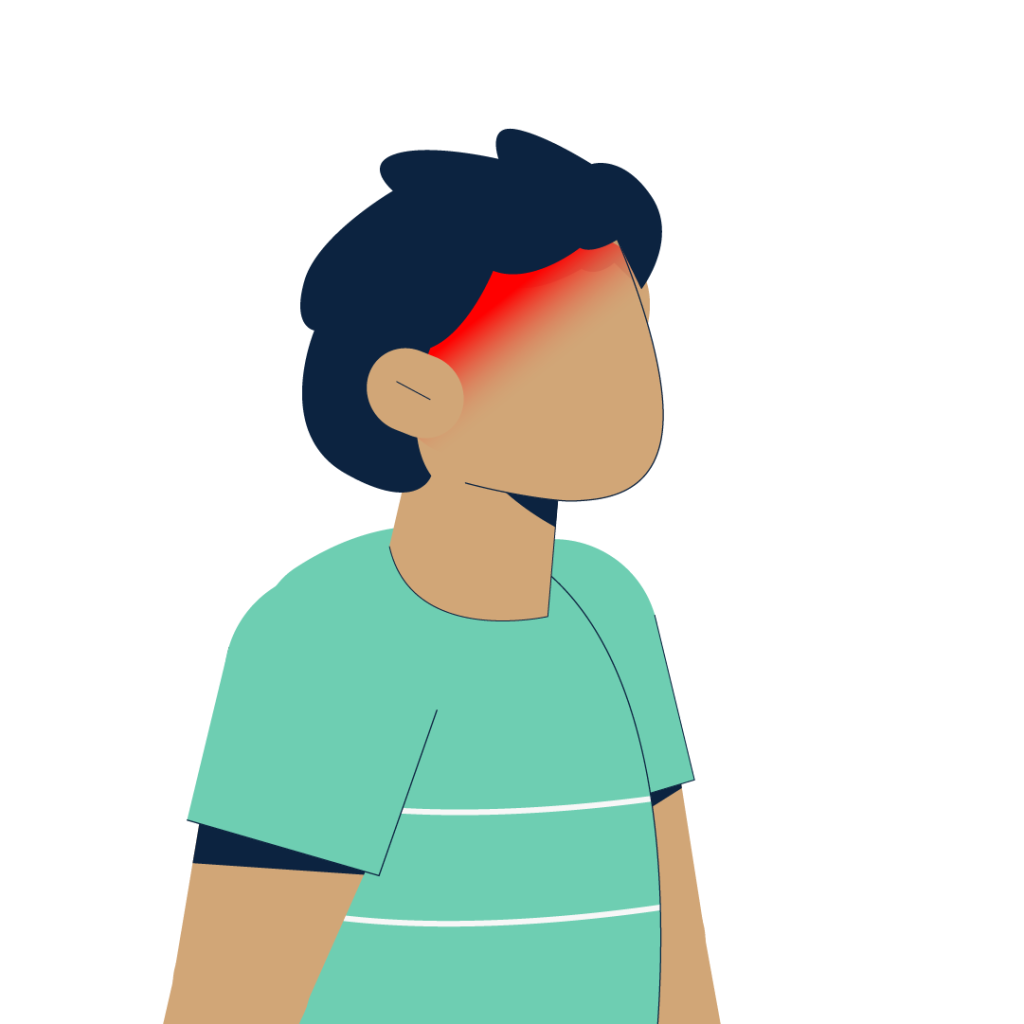

High fever
(may spike to more than 40°C)
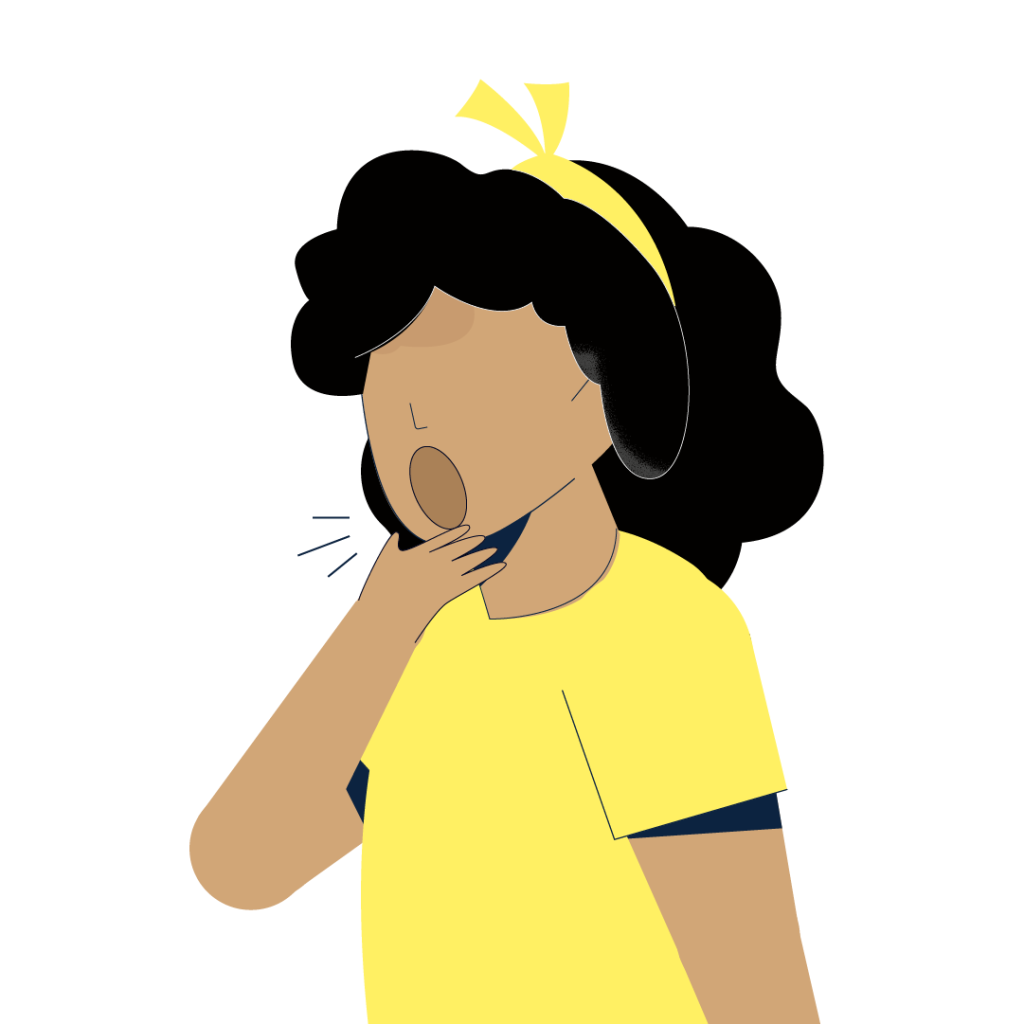

Cough
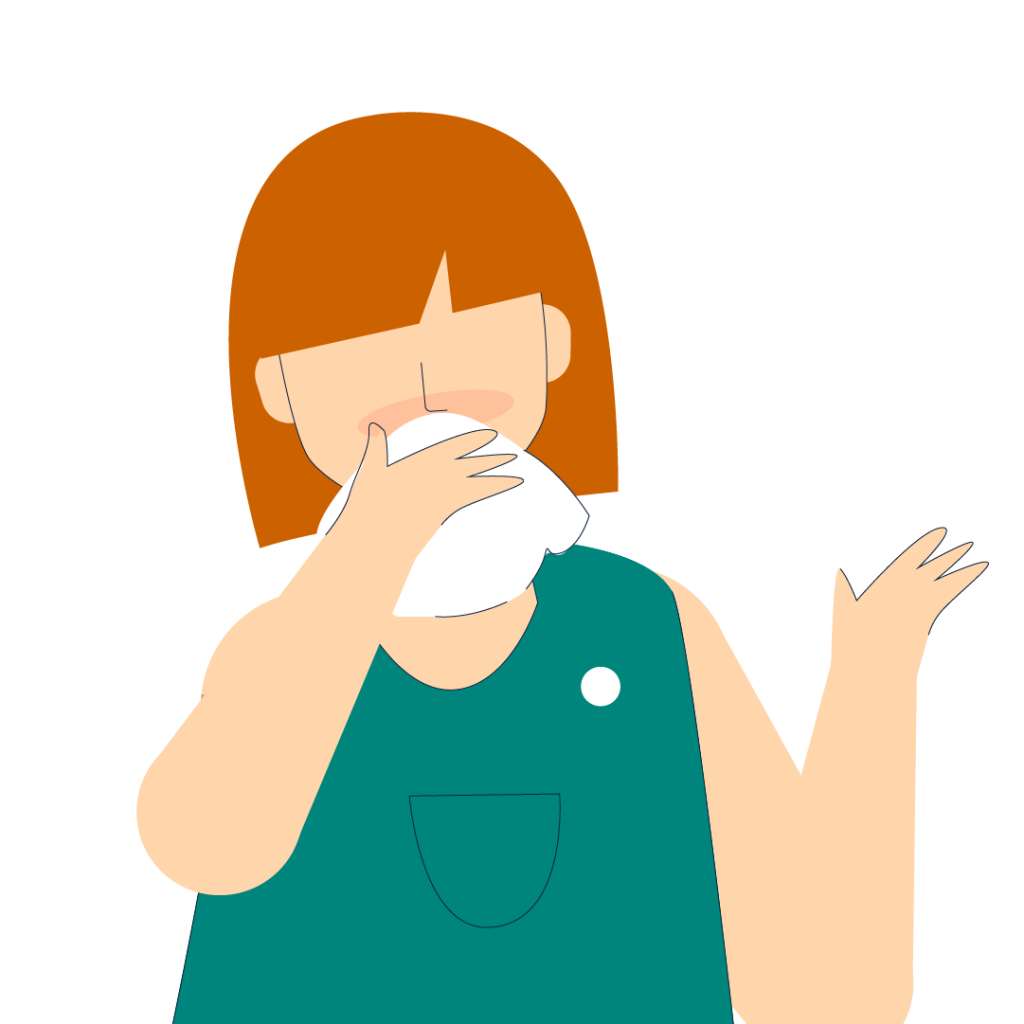

Runny nose
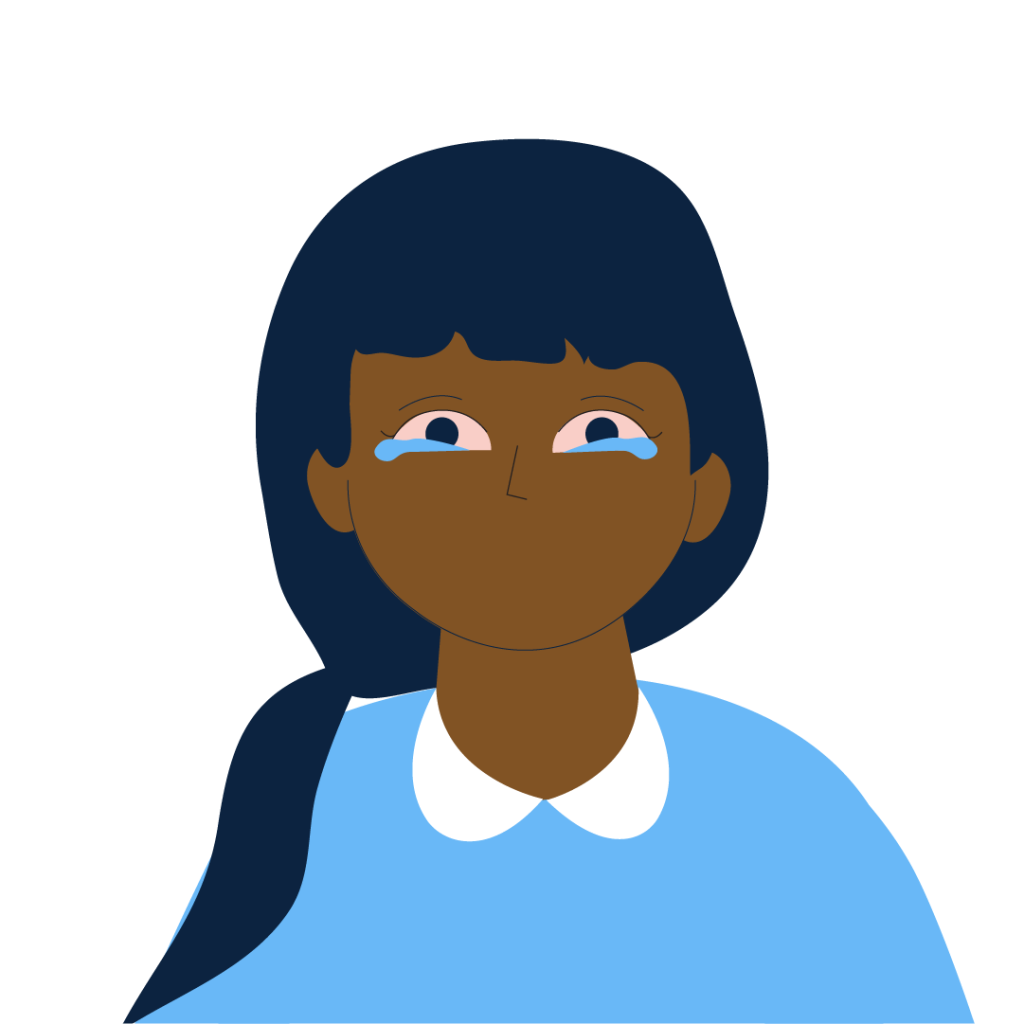

Red, watery eyes
(conjunctivitis)
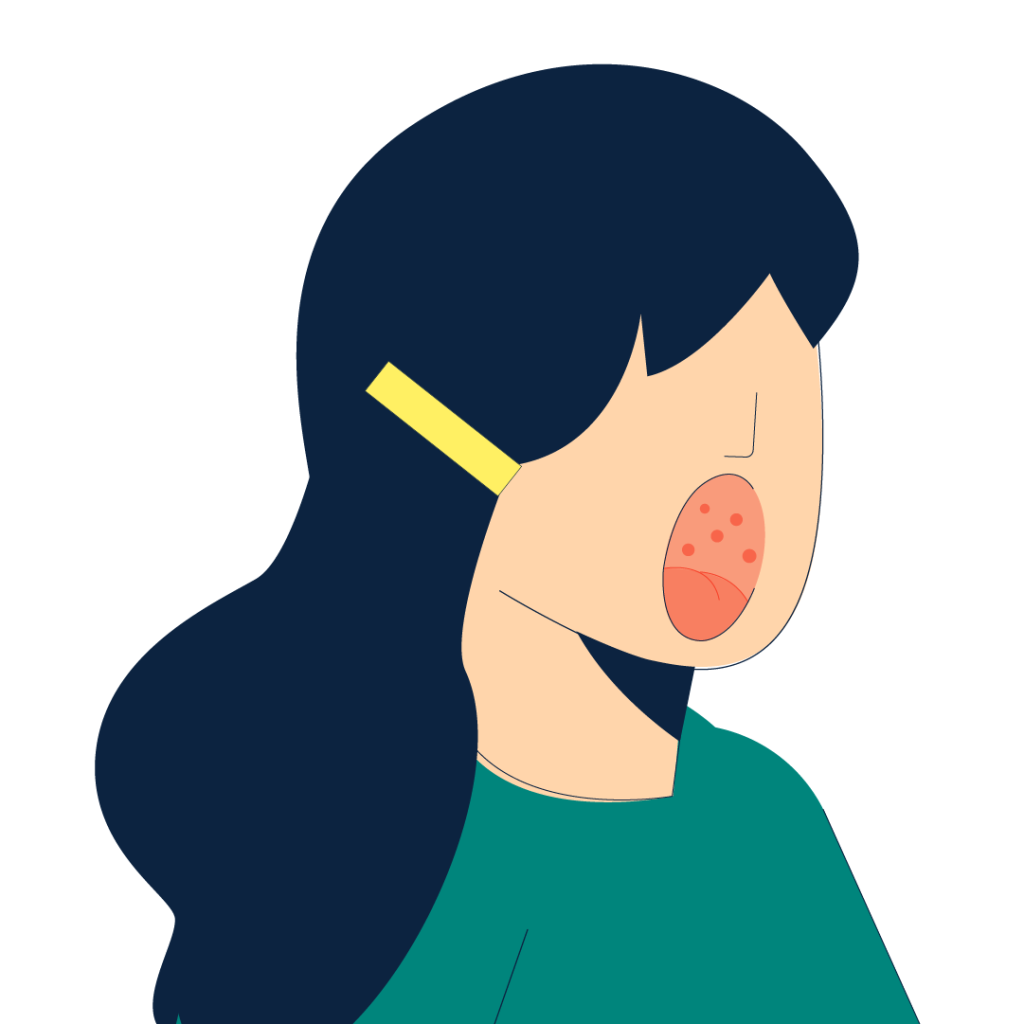
Spots in mouth
(2-3 days after symptoms begin)
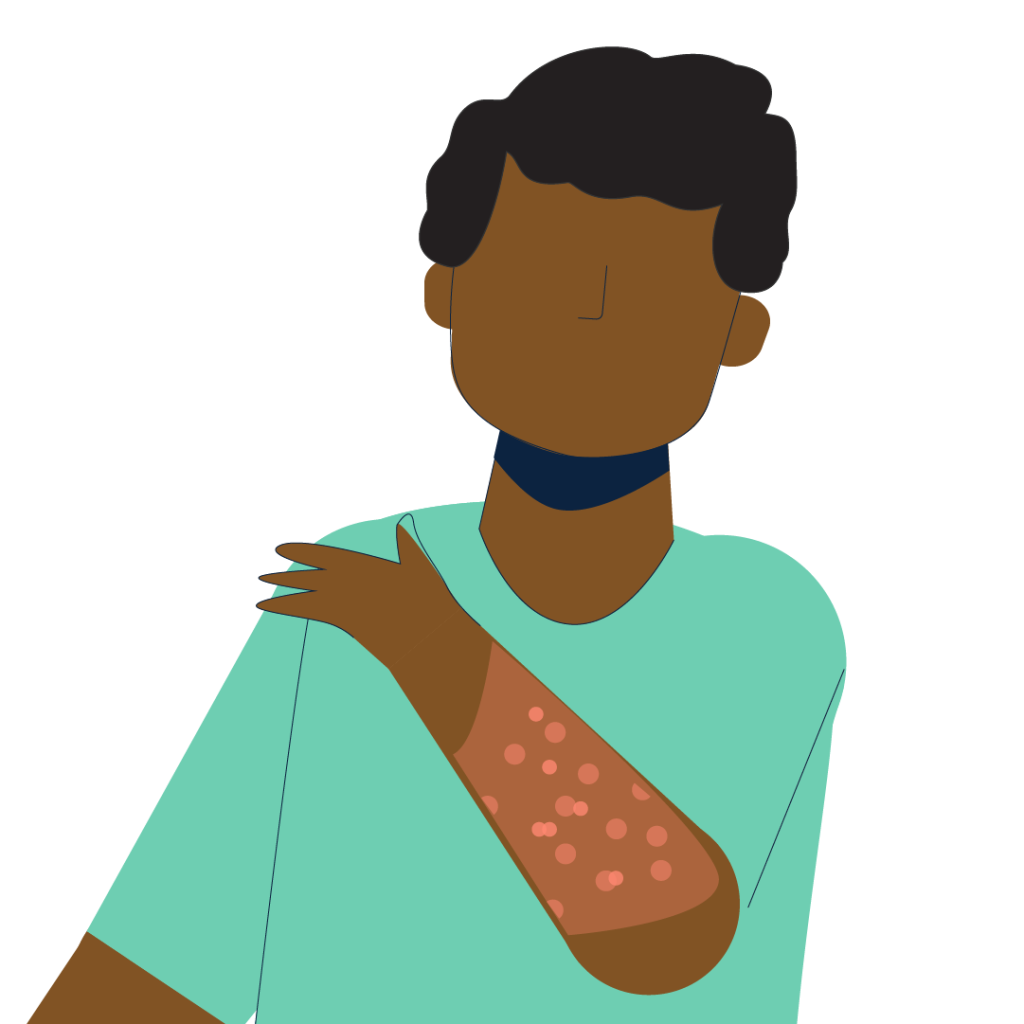

Rash
(3-5 days after symptoms begin)
How measles spreads
Measles can be serious and lead to complications
- Measles can cause serious health complications, affecting several organ systems such as ears, eyes leading to blindness, gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system including inflammation of the brain and death.
- Approximately 30% of reported measles cases have one or more complications, such as encephalitis or pneumonia.
- Each day, approximately 373 people die globally from measles-related complications, that equates to more than 15 deaths every hour as of 2023.
Understanding measles outbreaks
Natural disaster and/or conflict can put countries at greater risk for deadly measles outbreaks by damaging health infrastructure, interrupting health services and placing people in overcrowded residential camps.
In 2023, 321,582 cases of measles were reported globally, an 88% increase from 2022.
The proportion of children receiving a first dose of measles vaccine was 83% in 2023, well below the 2019 level of 86%.
The COVID-19 pandemic led to setbacks in surveillance and immunization efforts. Measles is often the first disease to resurge when pediatric vaccination rates drop, placing communities at heightened risk for preventable measles outbreaks.
Measles is still common in many parts of the world, and travelers with measles can bring the disease to countries that have largely eliminated it. Measles can spread rapidly.


